Children's illnesses cause parents more anxiety than their own. In autumn, winter, children become supercooled, they become more susceptible to infection. Sore throat often indicates the development of acute respiratory infections, but no less often there is a sore throat in children of school and preschool age. In order not to miss the time and start treatment on time, you should know how to recognize a sore throat from the first symptoms, depending on its form.
Angina is understood as tonsillitis in the acute stage. During the illness, inflammation of the fibrous tissue of the tonsils and palatine arches occurs, and the toxins released by pathogenic microorganisms affect the deterioration of the baby's well-being and contribute to the development of complications.
Causes of the disease
The inflammatory process occurs when an infection develops in the lymphatic tissue of the pharynx. According to various sources, in 90-95% of cases, the pathogen is a bacterium beta-hemolytic streptococcus group A. Infection occurs when communicating with sick adults and children. Streptococci are part of the conditionally pathogenic human microflora; they are easily transmitted by airborne droplets.
In most cases, acute tonsillitis in children is a complication of diseases caused by viruses:
- Rhinovirus causes inflammation of the tissues of the nasal cavity and oropharynx.
- Adenovirus is the causative agent of acute respiratory infections, multiplying in the mucous tissue of the conjunctiva, lymphatic tissue, and membranes of the upper respiratory tract.
- The herpes virus (type 1) infects the mucous membrane of the lips. Manifested by small transparent papules.
- Cytomegalovirus belongs to the family of herpes viruses and is capable of provoking the development of acute respiratory infections, inflammation of the hematopoietic system and the urinary system.
- Epstein-Barr virus (herpes 4) can be asymptomatic in the body or provoke the development of a number of diseases, including herpes, hepatitis, and nasopharyngeal cancer. According to statistics, in the United States, up to 95% of the population has been infected.
- Respiratory syncytial virus affects the lower respiratory tract of children and newborns. This occurs mainly in the cold season, with high humidity.
- The cause of a sore throat in a child from 3 years old is most often a streptococcal infection. Up to 1 year of age, children are protected by immunity transmitted by the mother. From a year to 3 years, sore throats caused by viruses predominate, and from 3 to 5 - bacteria.
Prerequisites for the onset of the disease
The variety of pathogens is the basis for differentiating the types of acute tonsillitis, but first it is necessary to understand why some children get sick often, while others have never experienced a sore throat.
After walking in the cool season, the baby complains of a throat, and cold drinks and ice cream are banned for him? The problem is immunity.
The most common causes of angina in children are as follows:
- Insufficient immune defense of the body. Susceptibility to infection directly depends on the condition of the tonsils, since they perform a barrier function. Infection, getting into the oral cavity, penetrates deep into the epithelial tissue. There it is met and neutralized by macrophages - immune defense cells, and immunity is slowly formed in the body.
- Past acute respiratory infections, stress, malnutrition - all this contributes to a decrease in immunity in a child, and the body loses in resisting the disease.
- Inflammatory processes in other organs. Caries, sinusitis, otitis media can cause the development of tonsillitis.
Hypothermia. Under the influence of low temperature, vascular permeability decreases, blood circulation is disturbed, and the immune defense of the child's body is reduced. - Chronic tonsillitis. If the baby has a "dormant" infection, which is repeatedly aggravated under the influence of adverse factors, then the cause of angina is chronic tonsillitis.
It is necessary to observe the breathing of the baby. With a curvature of the nasal septum, the presence of polyps in the nose, the risk of tonsillitis increases.

Symptoms and treatment of angina in children
Angina in a child is primary and disappears with its inherent pain and signs of intoxication and secondary, developing against the background of viral diseases or leading to a drop in immunity.
Common symptoms of angina in children:
- chills, temperature jump up to 39-40˚;
- gland enlargement;
- perspiration and dryness in the throat;
- swelling of the pharyngeal mucosa;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- abdominal discomfort;
- fatigue, aching joints.
Babies under one year old become irritable, restless, refuse to eat, sleep poorly.
Depending on the type of pathogen, 3 types of angina are distinguished: bacterial etiology, viral and fungal.
Read also: Decompensated chronic tonsillitis
According to the nature of the manifestation of signs of the disease, the following forms of angina in children are distinguished:
catarrhal- the most common and easiest form. Signs of a sore throat in a child are dryness and burning in the mouth. Intoxication of the body is expressed in weakness, headache, increased fatigue.
With this form of tonsillitis, there is often no temperature or it stays at the subfebrile level (37.1-38˚). The inflammatory process is expressed in redness of the tonsils, palatine arches, the appearance of a gray coating. This form is easily confused with SARS. The severity of the manifestation of symptoms directly depends on the age of the person, in children it is more difficult. The duration of the disease with proper treatment is 3-5 days.
Follicular is developing rapidly. The incubation period of the disease is 1 day. The main signs of a sore throat in children are an increase in temperature to 39-40˚ and a severe sore throat; often there is diarrhea, vomiting, clouding of consciousness.
At the same time, there is an increase in regional lymph nodes, the palpation of which gives the child pain. Gaps (gaps in the tissue) of the tonsils are clogged with gray-yellow purulent plugs. Subsequently, they open, the body temperature drops. This form of acute tonsillitis in babies is treated with antibiotics. The duration of the illness is about 7 days.
Lacunar has symptoms of follicular tonsillitis in a child, but even more intense. Purulent formations are easily removed with a spatula. The duration of the course of the disease is 5-7 days.
fibrinous. Its distinctive feature is the formation of plaque in the form of a white-yellow film covering the surface of the tonsils and palatine arches, which is why it is confused with diphtheria. Other symptoms are high fever, signs of intoxication.
Phlegmous angina is often a complication of follicular or lacunar tonsillitis. Its feature is the formation of a cavity with purulent contents on one side. The patient may tilt his head to one side, refuse food, feel weak. The temperature has risen significantly. Duration of treatment - about 14 days until the release of pus. The positive point is that children rarely get sick with it.
herpes. It is more common in younger children. Symptoms of herpes sore throat in a child are the presence of a small bubbling red rash on the tonsils. Tonsillitis of viral etiology develops rapidly, sometimes accompanied by severe pain in the abdomen, vomiting, and impaired stool.
Children aged 4 years and less complain not of a sore throat, but of a disorder in the digestive system.

Ulcerative necrotic. Deep ulcers form in the tonsils, covered with a greenish coating. If the pus is removed, the tissues begin to regenerate. In the absence of treatment for angina in a child, the tissues of the palate and larynx are involved in the process. The risk of complications with such tonsillitis is high, and the symptoms of the disease are mild.
Fungal tonsillitis in children rarely develops, accompanied by a temperature of up to 40˚ and the formation of a white cheesy plaque on the surface of the tonsils. This form rarely leads to complications, it is cured in a week.
All types of angina in children caused by fungi and viruses are atypical. Mixed forms are also distinguished, the treatment of which is hampered by the need for the complex use of antibacterial, antiviral and antimycotic agents.
Diagnosis and treatment of angina in children
Due to the high risk of complications, the treatment of angina in children under 3 years of age should be carried out on an outpatient basis. Convulsions, fever up to 40˚ - the basis for calling an ambulance.
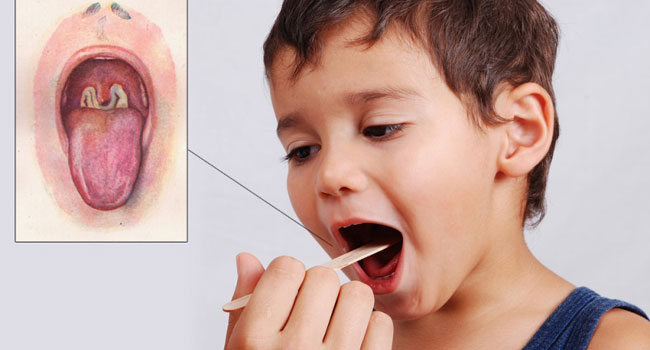
Diagnostics
Knowing the symptoms, it is easy to determine if the baby is sick, but there is a high probability of confusing acute tonsillitis with acute respiratory infections, diphtheria. Incorrectly chosen treatment tactics can lead to irreparable consequences, because antibiotics are powerless against viruses, antiviral drugs will not cope with a bacterial infection.
Upon examination, the doctor performs palpation of the lymph nodes, pharyngoscopy of the mucous membrane of the throat, prescribes the necessary tests:
- blood - to determine the level of ESR, leukocytes;
- smear to rule out diphtheria;
- smear from the surface of the pharynx for bacteriological examination;
- enzyme immunoassay to detect antibodies to viruses;
- analysis for antistreptolysin (ASL-O) to detect streptococcus in the body.
Based on the research, a diagnosis is made, treatment is prescribed.

Principles of treatment
The choice of treatment method depends on the form of the disease, the age of the child. The therapy is carried out under the strict supervision of a doctor on an outpatient basis or at home. It is important to use an integrated approach, at the same time using the means:
- antibacterial (antiviral, antifungal, depending on the type of pathogen);
- antiallergic;
- lowering the temperature;
- to normalize the intestinal microflora;
- physiotherapy (rinsing, heating in the absence of abscesses);
- enhancing immunity.
Read also: Catarrhal angina: symptoms, treatment, prevention
If adverse reactions occur, stop treatment and consult a doctor.
Important! After recovery, within a month you can not be vaccinated, including Mantoux.
Used drugs
Medicines for sore throats should cope with the elimination of the causes and symptoms of the disease: destroy bacteria, reduce body temperature, relieve sore throat, eliminate gastrointestinal disorders, neutralize allergic reactions, increase immunity, and quickly alleviate the baby's condition.
Bacterial tonsillitis in children is treated with antibacterial drugs included in the groups: penicillins, cephalosporins, macrolides.
Common penicillins include:
- Amoxiclav (DV amoxicillin) is produced in the form of tablets, powder for making syrup. It can be taken from the first days of life. Babies up to 3 months prescribe 30 mg / kg / day, and from 3 months to 20-45 mg / kg / day. The dose is divided into 2-3 doses according to the doctor's recommendation. For the treatment of angina in a child older than 6 years, the drug is prescribed in tablet form. The duration of treatment is 5-14 days.
- Augmentin (DV amoxicillin) is available in the form of tablets and powder for suspension. Children up to 3 months. prescribe 0.75 ml (single dose); up to 12 years of age take syrup or suspension.
Also in this group are used Flemoxin Solutab, Amoxicillin.

The group of macrolides for the treatment of angina in children includes:
- Azithromycin is a broad-spectrum drug, available in the form of tablets. Analogues of the drug: Azivok (release form - capsules), Sumamed (release form - tablets, capsules, powder for suspensions). According to the instructions, the dose of the drug is calculated based on the patient's body weight.
The group of macrolides is mainly used to treat tonsillitis in a child over 5 years old, as well as recurrent acute tonsillitis.
Effective antibiotics for angina of the cephalosporin group:
- Zinacef (DV cefuroxime sodium). The drug is administered intramuscularly and is used to treat acute tonsillitis in a one-year-old baby, as well as for an earlier age at the rate of 60 mg / 1 kg of body weight / day. Analogue - Aksetin.
- Zinnat (DV cefuroxime asketil) is available in tablet form and as a powder for suspension. Indicated for children from 3 months.
These drugs have proven themselves in the treatment of advanced cases of angina.
A positive result is obtained by using the antibiotic Bioparox in the form of an aerosol. For children older than 2.5 years, it is prescribed up to 4 times a day.
Despite the fact that in many instructions the start of taking antibiotics is considered to be infancy, in practice, first of all, penicillins are used, then macrolides, and for children with allergic reactions to these groups and older than 7 years, cephalosporins.
Only a doctor, guided by the results of a bacteriological study, can prescribe the most effective antibiotic, depending on the type of tonsillitis and the reaction of bacteria to the active substance of the drug.
Important! If after 3 days after taking antibiotics the patient's condition has not improved, you should consult a doctor and choose another drug.
Antihistamines
With tonsillitis, the risk of allergies increases. Even coloring substances in the composition of tablet shells or flavors in syrup can cause allergies, therefore, during treatment, it is recommended to use antihistamines: Suprastin, Zirtek, Zodak, Fenistil.

Probiotics
Antibacterial agents in the treatment of angina in children destroy not only pathogenic bacteria, but also beneficial ones. As a result, the work of the intestine is disturbed, dysbacteriosis occurs. Probiotics will help to establish the work of the gastrointestinal tract: Linex, Bifidumbacterin, Bifiform, Lactobacterin, Acipol.
Antipyretics
The body temperature during illness reaches 40˚, it can cause convulsions, therefore, with a sore throat in a child under 1 year old, the temperature of about 39˚ must be brought down. The tendency to convulsions is the basis for giving medicines even at a temperature of 37.5˚. Observing the approach of the mercury column to the critical mark, it is worth using the means:
- Paracetamol for children (analogue - Panadol syrup) is available in the form of suppositories and syrup. Helps relieve fever, eliminate muscle pain. It is used for children from 3 months. up to 12 years old.
- Kalpol (active substance (DV) - paracetamol). According to the instructions, it is used from 1 month.
- Efferalgan (DV paracetamol) is produced in the form of suppositories, syrup. It is prescribed for children from 1 month.
- Ibuprofen for children (DV of the same name) is a complex action drug that eliminates pain, inflammation, and fever. It has been used since 6 months. up to 12 years old. Analogues of the drug - Ibufen, Nurofen are used from 3 months. with a baby weighing at least 5 kg.




