How to treat adenoids in children at home is a question that is often asked by mothers of children aged 3–6 years. Adenoid vegetations often occur at this age and, without proper treatment, quickly develop, causing discomfort and worsening the health of the child. Overgrown adenoids make breathing through the nose impossible, which leads to hypoxia and the development of various complications - from appearance defects to developmental delay.
Meanwhile, if you seek medical help in time, the disease can be cured without resorting to surgery. Modern means make it possible to carry out conservative treatment with medicines, including folk remedies and physiotherapy procedures quite successfully at home, however, only an otolaryngologist (ENT) should prescribe treatment and control it.
Treatment of adenoids in children at home
Treatment is aimed at eliminating the causes of the disease, as well as getting rid of the symptoms. At home, for this, many diverse folk remedies can be used that need to be combined with classic drugs.
It has been established that as a result of breathing through the mouth, the body receives less than 20% of oxygen. First of all, the most sensitive organ to hypoxia, the brain, suffers from this.
Treatment begins with washing the nasal cavity. This procedure is aimed at washing out the infection (sanation), inflammatory exudate, as well as reducing edema and resuming airway patency. For this purpose, the following means are used:
- saline solution- the simplest and most effective remedy. A hypertonic solution is being prepared: dilute a teaspoon of salt in a glass of warm boiled water and mix thoroughly. Each nostril is washed with this solution 3-4 times a day, it should be washed until a clear solution is poured out of the nasal cavity, without mucopurulent secretions.
- pharmaceutical camomile. A decoction is being prepared: 1 teaspoon of dried chamomile flowers is poured into 100 ml of boiling water. Insist for one or two hours, then filter through gauze (in order not to filter, you can buy chamomile tea packaged in filter bags; in this case, take 1 filter bag for 100 ml of boiling water). Rinse the nasal passages in the same way as with saline.
- Calendula. An infusion is prepared: pour a teaspoon of dried calendula flowers with a glass of boiling water, leave for an hour (until it cools down), filter. The resulting infusion can be used to wash the nose, as well as gargle in the case when the palatine tonsils (tonsillitis) are involved in the inflammatory process.
Traditional medicine is effective only at the initial stage of the disease. If traditional medicine has not had the desired effect, or the disease is already in the second stage, pharmacotherapy is necessary.
The next stage of treatment is the elimination of inflammation - the main cause of airway obstruction. To do this, you can use the following natural remedies:
- Aloe juice- this plant has a whole arsenal of phytoncides that have antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects. The fleshy leaves of aloe are cut, kept in the refrigerator for about 6 hours, then wrapped in gauze and squeezed out the juice. If the child is 3 years old or more, then he can instill pure freshly squeezed aloe juice 3-5 drops into each nostril. Children under three years of age are instilled with aloe juice, diluted in boiled water in a ratio of 1: 1. Aloe juice quickly loses its medicinal properties, so it is recommended to squeeze fresh juice before each procedure.
- Eucalyptus essential oil. Eucalyptus oil has a powerful antiseptic effect, but pure oil is not used, as it can cause burns to the mucous membrane and an allergic reaction. Before use, it is stirred in a neutral solvent, vaseline or refined vegetable oil can play its role. 3 drops of essential oil are dripped into a teaspoon of the solvent, mixed. The resulting mixture is instilled into the nose - 2-3 drops 2-3 times a day.
- Propolis. This is an effective remedy, but it can only be used if the child is not allergic to bee products. Take one teaspoon of propolis, add 10 teaspoons of refined vegetable or butter, melt in a water bath until the ingredients are completely dissolved. After cooling, an ointment is obtained, which is lubricated with each nostril with a cotton swab. You can also lower the cotton turunda into the ointment that has not yet solidified, then cool it and plug the nasal cavity. Tamponade time should exceed one and a half hours.
- Tui oil. One of the most popular treatments for adenoids in children. It is used at a concentration of 15%. Thuja oil is dripped 2-5 drops into each nostril three times a day. Children under 3 years old are recommended to dilute the oil with water.
- Celandine. The decoction is prepared by pouring two tablespoons of the dry mixture and two glasses of water and boiling for 10-15 minutes over low heat. The resulting liquid is cooled, filtered and used for washing the nose and gargling.
- Sea buckthorn oil. The oil is dripped 2-3 drops into each nostril twice a day. The course of treatment takes two weeks.
- Carnation. A decoction is prepared from ten buds and half a glass of water. Boil, infuse for 2 hours, cool and filter. Clove decoction is instilled into the nose 3 drops up to 4 times a day. Treatment of adenoids in children with cloves is recommended by Dr. Komarovsky.
The course of treatment of adenoids at home can be supplemented with immunostimulating herbal preparations, for example, echinacea. Echinacea extract can be purchased at a pharmacy, or you can prepare it yourself. To do this, 100 g of raw materials are poured into 1 liter of boiling water, insisted for 2 hours, then filtered. The decoction is taken orally 50 ml three times a day. This remedy should not be used to treat children under 1 year old.
Contrary to popular belief, hot air inhalations, steam from boiling solutions of medicinal herbs or boiled potatoes should not be done.
Traditional medicine is effective only at the initial stage of the disease. If traditional medicine has not had the desired effect, or the disease is already in the second stage, pharmacotherapy is necessary. Treatment is predominantly local. According to indications, antiallergic drugs are prescribed (allow to reduce swelling), anti-inflammatory, vasoconstrictor drugs. With the development of adenoiditis, systemic drugs, including antibiotics, antipyretics, may be prescribed.
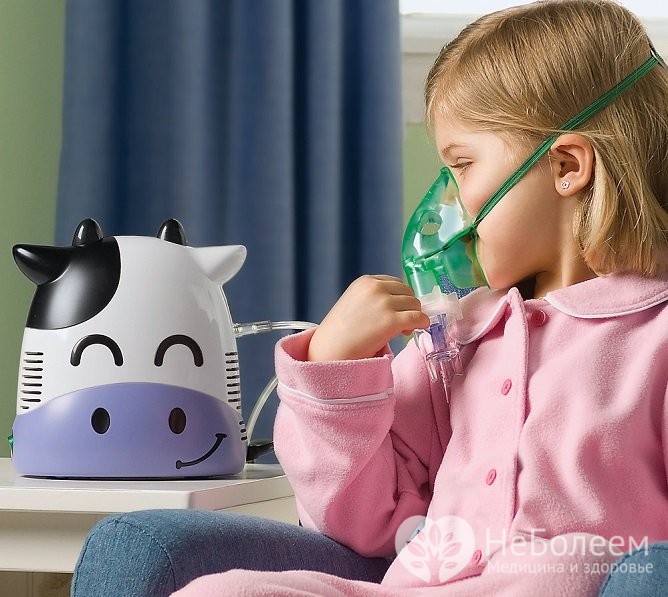

At the stage of chronic inflammation, home treatment is supplemented with physiotherapy. Inhalations, UHF therapy, electrophoresis, UV irradiation are used. Inhalations of warm air with drugs improve circulation in the tissues and relieve swelling. UHF (ultra-high-frequency current) is used to warm up the thickness of tissues and improve their metabolic processes. With the help of electrophoresis, drugs are delivered directly to the focus of the disease. UVR contributes to the sanitation of the mucous membrane.
In addition to therapy with home and pharmacy medicines, breathing exercises are often prescribed, which, without side effects, helps to restore the patency of the nasal passages and eliminate hypoxia. Breathing exercises allow for effective treatment of children at home without surgery, but they must be carried out regularly, daily, for 3-4 weeks, and sometimes longer. The gymnastic respiratory complex is usually selected by a doctor, you can use the ready-made Strelnikova respiratory gymnastics complex, which was developed for singers who have voice problems, but has demonstrated its effectiveness in the case of other respiratory diseases, including in children.
At the stage of chronic inflammation, home treatment is supplemented with physiotherapy. Inhalations, UHF therapy, electrophoresis, UV irradiation are used.
It is important to pay attention to the microclimate in the room - the air temperature should be in the range of 18-20 ° C, while taking care of the humidity in the room, which should reach 60-70% (dry air helps to maintain inflammatory processes). In some cases, it is advisable to use a humidifier. Wet cleaning should be carried out regularly. Sea air has a good therapeutic effect.
Children with adenoids are not recommended to take hot baths, go to the bath and generally overheat the body, especially during the period of exacerbation of adenoiditis. You should also avoid very hot and very cold drinks, as well as drinks and foods that irritate the mucous membrane (sour, spicy, spicy). Hypothermia is contraindicated.
Contrary to popular belief, hot air inhalations, steam from boiling solutions of medicinal herbs or boiled potatoes should not be done. Only warm steam is allowed, for which a nebulizer is used.
Topical application of an alcoholic solution of iodine to the mucous membrane of the nasal passages and nasopharynx can be dangerous.
What causes the development of adenoids
Adenoids are compensatory hypertrophy of the pharyngeal tonsil, its increase in response to chronic or frequent acute inflammation.
The tonsil is a large accumulation of lymphoid tissue in the nasopharynx, dressed in an epithelial capsule. This formation protects the upper respiratory tract from infection, so it is the first to take a hit. In conditions of insufficiently developed immunity in children, the tonsils do not always cope with their function, they often become inflamed. Constant stimulation (infectious or allergic inflammation) contributes to an increase in the volume of lymphoid tissue. So the children's body compensates for the functional insufficiency of the amygdala, so they talk about compensatory hypertrophy.
You can use Strelnikova's ready-made respiratory gymnastics complex, which was developed for singers who have problems with their voice, but has demonstrated its effectiveness in the case of other respiratory diseases, including in children.
Normally, after an immune response, the amygdala returns to normal size. But often in conditions of excessive activity, the tissue is depleted and remains hypertrophied.
Separately, it is worth highlighting the inflammation of the nasopharyngeal tonsil - adenoiditis. This condition develops faster than adenoids, but responds well to treatment with antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs. Differential diagnosis is carried out by a doctor, but the difference can also be seen in systemic manifestations - elevated body temperature, deterioration in the general condition of the child with adenoiditis.
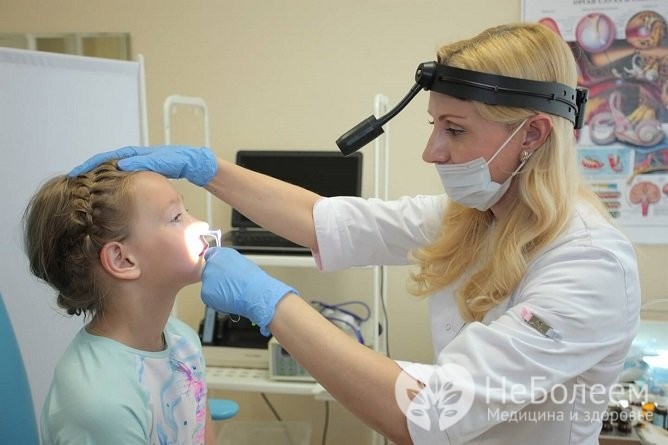
How to determine adenoids in a child
The process of tissue hypertrophy is long and takes more than one month, so it can be difficult to notice adenoids in the early stages. The first clinical manifestations occur when more than a third of the respiratory passage is blocked by adenoids - that is, when hypertrophy has reached the second and third degree. Then the following symptoms occur:
- loud sniffing when breathing;
- snoring for no apparent reason (runny nose, nasal congestion, swelling);
- sleep apnea (short-term cessation of breathing) in a dream, followed by several deep reflex breaths, the child literally gasps for air in a dream;
- a noticeable deterioration in nasal breathing, the child breathes through the mouth, which is why the mouth is constantly ajar;
- change in the timbre of the voice, which becomes less sonorous;
- nasality, the child says "in the nose";
- deterioration of sleep - the patient cannot fall asleep for a long time, wakes up several times a night;
- decreased physical activity, fatigue, lethargy in the morning, deterioration of endurance and physical qualities;
- cognitive impairment - memory impairment, increased reaction time to sensory information, mental decline;
- hearing loss, frequent otitis.
Children with adenoids are not recommended to take hot baths, go to the bath and generally overheat the body, especially during the period of exacerbation of adenoiditis.
If in adults this disease mainly causes discomfort and only occasionally complications occur, then in children long-term adenoids can lead to irreversible consequences. The point is a hypoxic state - an insufficient amount of oxygen due to the lack of nasal breathing. It has been established that as a result of breathing through the mouth, the body receives less than 20% of oxygen. First of all, the most sensitive organ to hypoxia, the brain, suffers from this. It actively develops in children, so its oxygen requirements are even greater than in adults. The most dangerous prolonged hypoxia for children under 5 years old, it can lead to developmental delays, both mental and physical.
Due to constant breathing through the mouth, the structure of the facial skull changes, the nasal conchas are deformed, and a characteristic “adenoid type” of the face is formed with an elongated oval and a changed shape of the mouth. The shape of the teeth and dentition, the bite also suffers, the cartilaginous elements of the skull change.
It is important to diagnose the disease in a timely manner and actively treat it, the sooner treatment is started, the greater the chances for the success of conservative therapy and the full recovery of the body.
Video
We offer you to watch a video on the topic of the article.




